Nationalize AI - Part 2 - Labor
07 Dec 2024 Reading time: 6 minutesThis is Part 2 in a multipart series on nationalizing AI:
- Nationalize AI - Part 1 - Defining The Problem
- Nationalize AI - Part 3 - Corporate Power
- Nationalize AI - Part 4 - Inefficient
- Nationalize AI - Part 5 - Superiority
- Nationalize AI - Part 6 - Conclusion

Labor
Overall, my thesis regarding labor and AI, for the purposes of this article, is broken down between two major points - ethics and employment. There’s plenty of interchange and correlation between the two, however specifically breaking it up here will allow me to be more pointed, especially about a specific ethical problem.
Ethics of Stealing
A critical foundation of the recent developments in AI is the data that is used for training. The specifics of how it is used and it’s part of the process here is less important than the fact that this data is largely publicly available data generated by billions of humans.
Ethically, how is it acceptable to do the following:
- Use data generated by billions of humans
- A lot of which is copyrighted, by the way!
- Create an AI system that uses that data
- Profit by charging businesses and other people for use of the system
- In reality, currently, a lot of the money is from venture capital, but the same ethical issue persists (or perhaps is even worse?).
Granted, a lot of the data is not generated necessarily by citizens of the USA - which is an interesting counterpoint; although my response to that is that should be globally owned instead of by any one nation. But for now, that seems far more impractical. Nationalization would likely be a critical first step towards globalized ownership, anyway.
While this is already a problem - profiting by using the free labor of others (who generated this data) at this scale - this only gets worse as the systems improve.
Billions of people contributed, and the CEO of OpenAI is driving a car around that costs 5 million dollars.
Unethical.
Employment
We do know, that these AI systems are useful for various tasks. I’ve used ChatGPT, for example, a lot of people have. It is useful! The usefulness is already resulting in increased productivity in a lot of industries.
Overall, as a society, we do want productivity to increase, so what is the problem?
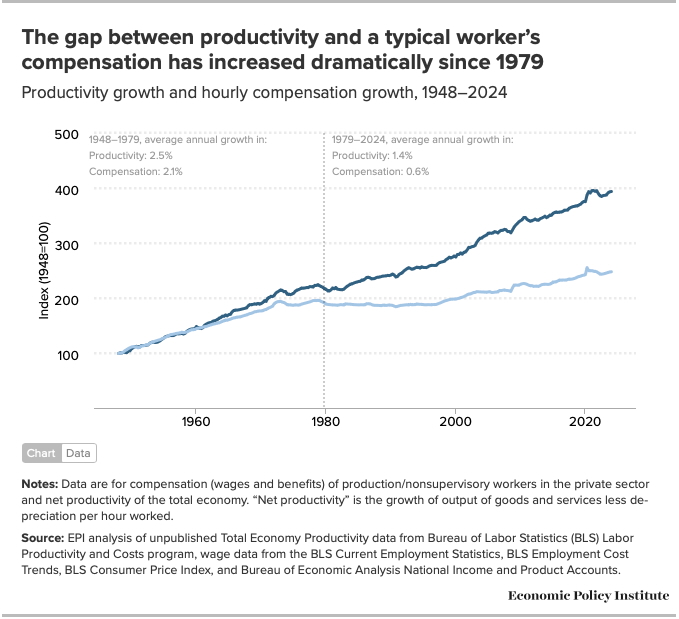
Let’s take a step back and talk about, largely, non-AI related productivity gains. Other technologies, process improvements, etc. A critical issue we’ve been facing - which has led to historically bad inequality - is that productivity gains are not being met with the same % of an increase in wages, and it’s getting worse:
By the way - this is not strictly a partisan issue. Control of the presidency and congress have been both parties during this time frame (1979 - 2024), although it really started accelerating around when Reagan’s policies started (which Democrats & Republicans have refused to address / fix because of their corporate donors - but that’s a topic for a different day).
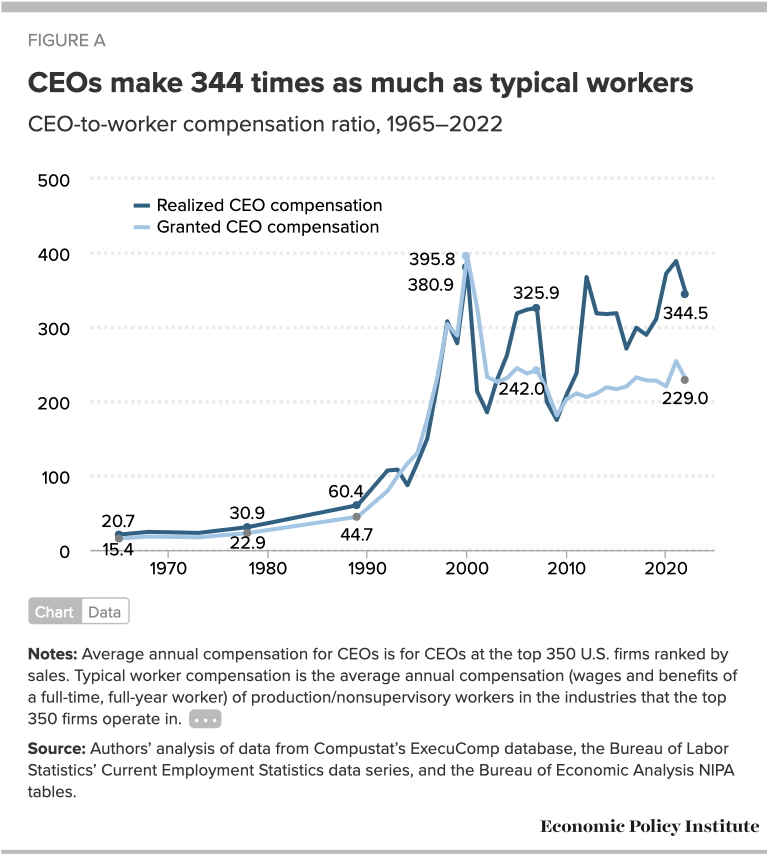
There’s many different angles to this, and it involves multiple groups in the upper class (shareholders, as well, for example) - but here is one example that is particularly stunning.
The two lines are realized vs granted compensation for CEOs represented as multipliers of the typical worker in their respective industries. The difference between realized and granted (the two lines) are not especially important for the context of this section. The main point here is that before 1980 - CEOs made “only” ~31 times the typical worker and now it’s over ~344 times as much. Note, the footnote in the image says this but this data is from the top 350 companies in the country specifically.
This is not a post primarily about income inequality - but it is critical to my thesis to show that productivity gains are not going to the average worker but to the members of the upper class.
Critically, I am not claiming nationalizing AI will solve this preexisting problem; but that it will prevent it from becoming worse due to the actions of private AI companies.
Effects on Employment
Short and Medium term
The effects on the labor market have already started. Increased productivity is common in many industries, as I mentioned before. As we know - the outcome of productivity gains are not resulting in rewards for workers, but rather increasing compensation for CEOs and shareholders. Nationalization of AI would ensure this is not the case.
While it is true that some segment of the affected labor force can shift, for now, this will not be the case forever.
Long Term
Despite my focus here on the current/short term effects on the labor market - it is my opinion that over some longer time frame, that AI will certainly be able to do every single job. This is a marked difference of AI versus new technologies in the past (printing press, internet, etc) which generated or shifted jobs in new or other sectors. An infinitely duplicatable, more-than-human-capable AI does not leave room for any job for any human.
The Long Term Is Likely Relatively Short
OpenAI is already talking about how AI could replace all / subsections of the labor force:
- “He’s going to be right there at the beginning of it, maybe even as things like AGI, we get there,” she (OpenAI Chief Financial Officer Sarah Friar) said on Tuesday, referring to autonomous systems that surpass humans in most economically valuable tasks. Source
- The time frame being referred to here is within the next 4 years (!!!!!!)
- “I want the door open to everything,” Friar said in an interview, when asked about a recent report that the company has discussed a $2,000 monthly subscription for its AI products. “If it’s helping me move about the world with literally a Ph.D.-level assistant for anything that I’m doing, there are certainly cases where that would make all the sense in the world.” Source
- “OpenAI CEO Sam Altman and Chief Technology Officer (CTO) Mira Murati said last fall that AGI will be reached within the next 10 years.” Source
- As previously mentioned, this is the point where most/all economically valuable tasks could be performed by AI.
This is coming soon.
Nationalization
To fully round out the earlier point on ethics for a second, it is wholly unacceptable that people and companies are getting rich by stealing from everyone and then benefiting from workers’ productivity gains and/or obsoleting their jobs.
In summary - the socialization of AI’s benefits, which in my view requires nationalization - is necessitated for these reasons:
- AI is already driving significant productivity gains in the labor market. However, as demonstrated earlier, the fruits of productivity gains, of course including those predating AI, have not been shared equitably with workers.
- Over a longer period of time, it is clear that AI will make humans obsolete for labor.
- These systems are built upon the stolen labor outputs of everyone.
This is only part two of the series, but in my estimation - already - these issues alone prove my thesis on the necessity of nationalization.
In the next part of this series, we will explore how corporate consolidation of power further necessitates the nationalization of AI: Nationalize AI - Part 3 - Corporate Power